
The bigger tape library has multiple drives, and the robotic tape loader can access all of them, improving reliability. Backup tape autoloaders provide automatic tape exchanges and more reliability than a stand-alone drive, but still have a limited capacity compared to tape libraries.Ī tape autoloader typically consists of a tape drive, a tape magazine and a robotic arm that moves tapes between the drive and the magazine. Tape libraries offer more capabilities than autoloaders, but are often far more expensive, as well as more complex because they have more tape drives.Ī tape autoloader is a step up from a single tape drive for backup and archiving. Tape libraries and autoloaders automate backups and archives with multiple tapes. For example, old tape drives may not work with a new library.
As technologies develop, an organization must ensure its tape library is compatible with all the other necessary components. Tape libraries can get complex, requiring management by the system's backup software.

Because of the sequential nature of tapes, a user must roll through a tape to locate specific data. Though LTFS has improved filing systems and accessibility, a tape library can't match the access speeds of other technologies, such as disk.

Retrieval of data from a large backup tape library can actually be faster than retrieving data from the cloud. With the explosion of data estimated to hit the level of multiple zettabytes by 2020, enterprises often turn to tape for long-term archiving. For example, one LTO-7 tape cartridge holds up to 6 terabytes (TB) of native capacity, or 15 TB compressed. Tape libraries contain the capacity for massive amounts of information that is rarely accessed or changed. Encryption is especially important when tapes go off site because it protects the data in the event of a lost or stolen tape. In a common scenario, a backup media server, tape library, virtual tape library ( VTL) or individual tape drive encrypts data as it is written. In a disaster recovery situation, tape is a useful tool for retrieving data.Įncryption is offered for data security with tape libraries. Tape is also attractive for its durability and shelf life. Disk, for example, is expensive for archiving because of both upfront and operational costs. Benefits and drawbacks of tape librariesĪ tape library's cost is generally less than disk or flash systems. A large enterprise will often use a tape library as a secondary backup target or an archive, if not as a primary backup means. Organizations of all sizes use tape libraries.
PIXAVE LIBRARY BACKUP ARCHIVE
The Linear Tape File System ( LTFS), for example, puts a file system on top of a tape library, improving its suitability for archive use cases. Though advances in technologies, such as large-capacity disk drives and the cloud, have made tape less fashionable as a backup device, it is still a popular choice for archiving. Tape drives were the standard backup targets for decades. In determining specifications for a tape library, an organization must typically figure out how big the library backup or archival set will be, including factoring in data growth.
PIXAVE LIBRARY BACKUP SOFTWARE
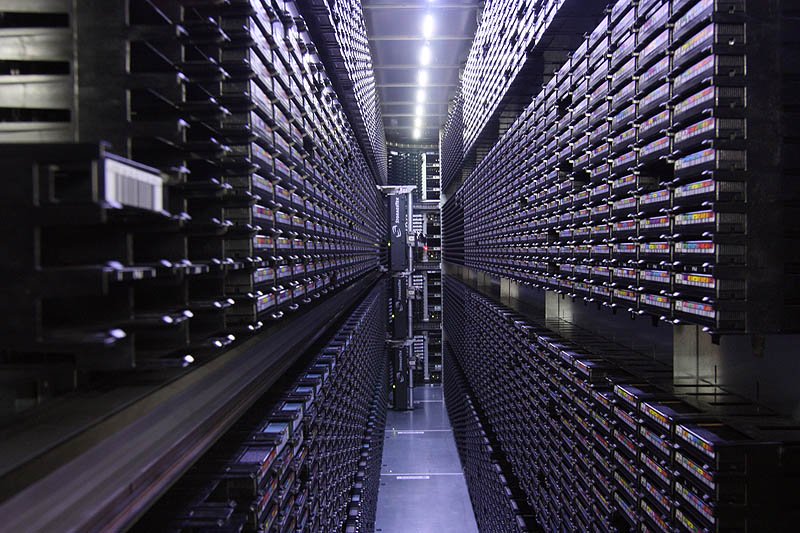
Tape library vendors provide compatibility lists of which backup software and hardware will work with their products. What tape libraries are used for and how they workĪlthough tape drives have improved in features and reliability, the concept of writing data to magnetic tape has not changed for decades.Ī tape library and its features must be compatible with the rest of an organization's data protection system, including the backup software. A library can include hundreds, or even thousands, of tapes. A typical library contains multiple tape drives for reading and writing data, access ports for entering and removing tapes, bar codes to track the tapes, and a device for mounting and dismounting tape cartridges. Tape libraries vary widely in cost and complexity. In data storage, a tape library is a collection of magnetic tape cartridges and tape drives.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
